Published Mach 2021
Jennifer Doran, MD 1, Josephine Cool 2
1 Resident, Internal Medicine, University of Colorado, 2 Instructor at Harvard Medical School, Director of Procedural and Ultrasound Education in Hospital Medicine and Director of Ultrasound Education for Internal Medicine Residency, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Objective(s)
- Identify A-lines on lung ultrasound and integrate the finding into a diagnostic framework for evaluating dyspnea.
- Describe the ultrasound signaling process that generates the reverberation artifact of A-lines.
Teaching Instructions
Plan to spend 5-10 minutes familiarizing yourself with the animations of the PowerPoint and the key findings of this POCUS clip.
Instructions: Download the PowerPoint presentation file (the video may not work in the browser viewer) and have the image pulled up in presenter mode before learners look at the screen, to avoid revealing the diagnosis. Ask a learner to provide an overall interpretation. Then advance through the animations to prompt learners with key questions and reveal the findings, diagnosis, and teaching points. You can go back to prior graphics and questions by using the back arrow on the keyboard or by scrolling back on the mouse wheel.
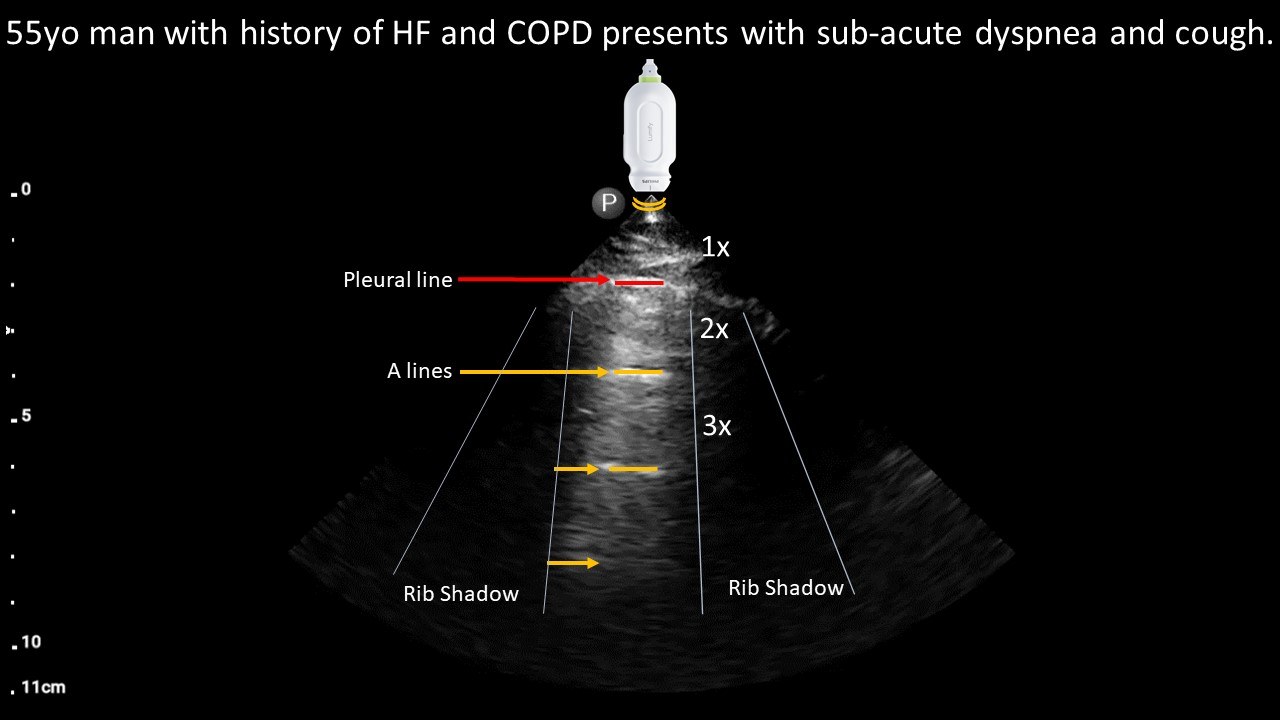
POCUS image interpretation:
Normal lung sliding = normal pleura
A-profile = aerated lung deep to the visceral pleura in this specific window.
Diagnosis: Likely COPD exacerbation based on the clinical stem and normal lung sliding with a-profile on POCUS.
Teaching:
-A-lines on lung US is a recurring artifact produced by back-and-forth reflections of US waves between the air in the chest and the transducer.
-A-lines with no lung sliding = air in the pleura or diseased pleura with aerated lung.
-A-lines with normal lung sliding = well-aerated lung just deep to the visceral pleura in that specific window. Alternatively, increased density in the same window would produce B-lines
Presentation Board
Take Home Point
- A-lines on lung US is a recurring artifact produced by back-and-forth reflections of US waves between air in the chest and the transducer.
- A-lines with no lung sliding = air in the pleura or diseased pleura with aerated lung.
- A-lines with normal lung sliding = well-aerated lung just deep to the visceral pleura in that specific window.
References
“ACP POCUS 3: Lung Ultrasound.” ACP, 1 Oct. 2022, www.acponline.org/cme-moc/online-learning-center/acp-pocus-3-lung-ultrasound.